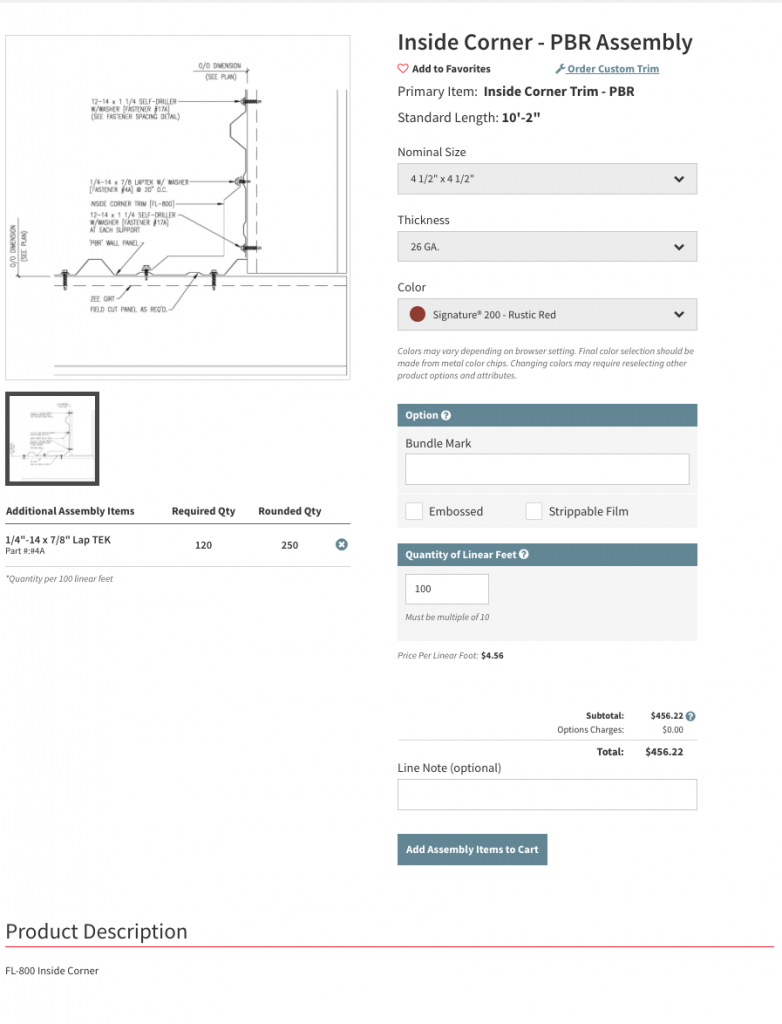
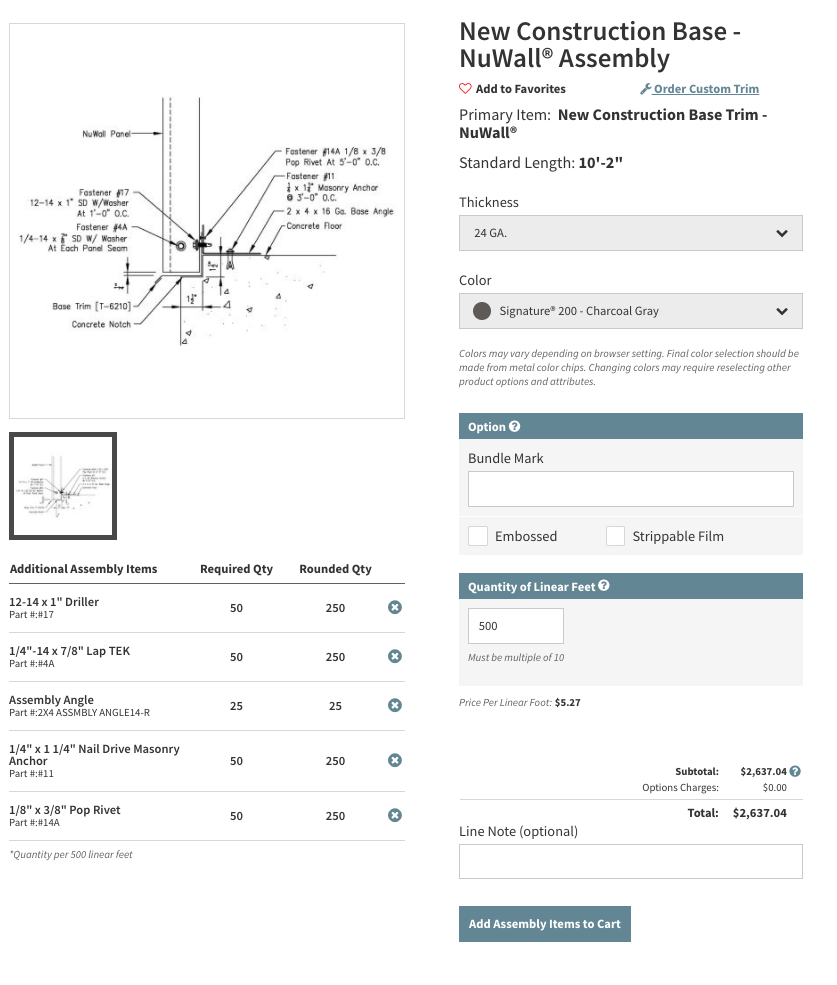
The recent arctic blasts that hit the northeast brought to mind many things: hot cocoa, the evils of shoveling snow, a nice fire, the longing for a warm beach and, of course, how to properly specify snow retention systems on standing seam roofs. I’m not alone here, right?
All jokes aside, when I was scratching my brain for a new blog post, the cold weather and blizzards reminded me how easy it is to specify snow retention devices improperly. It might appear rather elementary at first; you might think it is as simple as planning for snow retention around entrances and frequent walkways. If so, you, along with many others, are mistaken. Let’s review some not-so-obvious areas to consider while planning a snow retention system for a standing seam metal roof.
Gutters
If a gutter is used that has a face high than the pan of the metal roof panels, the gutter must be protected from sliding ice and snow. Gutters are designed for one purpose – to channel the water to a downspout. If it is left unprotected it cannot resist sliding ice and snow.
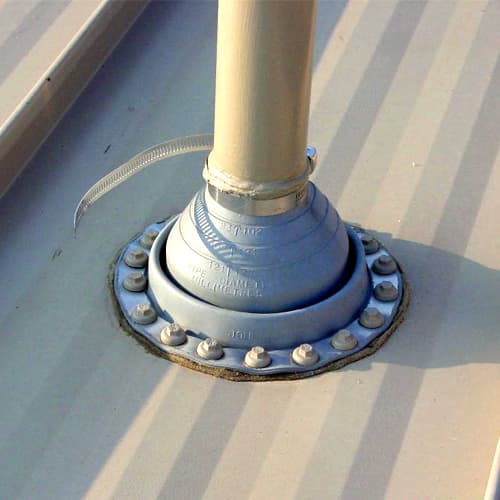
Pipe penetrations
As ice and snow slides down a roof and encounters a pipe penetration, the force can cause the pipe to move down slope and damage the roof jack and the roof, or shear the pipe at the roof surface.
Upper roofs draining into lower roofs
The upper roof should have a snow retention system installed to prevent ice and snow from falling onto the roof below. Without snow retention, the sliding ice and snow can cause extensive damage to the roof membrane and to equipment on the lower roof.
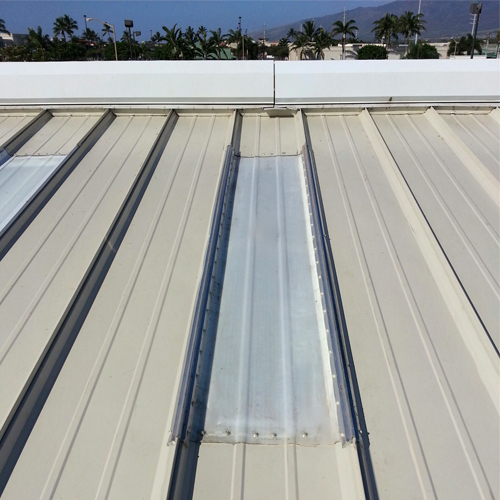
Panel seams perpendicular to the main roof slope
Connector roofs or dormers are typical examples of this type of roof area. The main roof slope provides a surface for ice and snow to slide toward the eave. If it then encounters a roof surface that is perpendicular to this main slope, damage to the roof panels and trim on these roof areas can occur.
Valleys in high snow load areas
Valleys allow for snow to slide down a surface that is perpendicular to the panel seams. This offers the potential to bend panel seams down or shear them from the panel.
Aside from considering these areas while planning your snow retention system, also use clamps instead of screws to attach the system to the standing seams of the roof panels. Screws not only perforate roof panels but can also pin the roof and prevent it from floating as designed. Clamps, by comparison, have been tested and can be engineered for the specific roof to which they will be attached, allowing for the snow load, roof slope, panel run length and other details. These clamps do not penetrate the roof membrane, do not hinder roof expansion and are easily installed with a screw gun.
Final Recommendations
Lastly, I recommend having a registered, professional engineer design a retention system that meets the specified snow loads for the project. Without their expertise, there are possible repercussions. If the snow retention system cannot support the snow load, it can result in an entire system failure and major roof damage. This could potentially cause snow and ice to fall and hurt bystanders.
By keeping all of these in mind, along with proper installation and maintenance, a snow retention system will help your SSR survive winter blasts and protect pedestrians, too.