Insulated metal panels (IMPs) used for building envelopes offer great simplicity in terms of enclosing a building in an attractive, energy-conscious manner. However, they require somewhat different thinking in terms of design and installation compared to conventional single skin panels on metal building with separately installed fiberglass insulation and vapor liners. That’s because, while the insulation aspect of IMPs is well controlled in the factory, the air and vapor sealing aspects are entirely in the hands of the installers in the field.
Why is vapor sealing a concern? Because it can make or break a building envelope. Airborne moisture that travels through seams, joints, or gaps between IMPs or between the panels and the structural steel can condense and wreak havoc on the integrity of the wall system. If that condensed moisture makes its way to unprotected edges of metal, then rusting, staining, and deterioration can occur. If it collects and drains out the bottom of the panel, then a building owner may mistakenly think that the IMPs are leaking water. If the moisture works its way inside a panel and becomes trapped it could freeze in cold climates or applications, and push panels enough to make unsightly or fail to perform as intended.
How does an installer of insulated metal panels avoid these issues? By properly using sealants as recommended by the IMP manufacturer to close the gaps and assure a vapor-tight installation. Here are the key things that installers need to pay attention to:
Sealant Types
In most cases, butyl caulking is the recommended sealant for panel joints and perimeter attachments, although urethane sealant may be called for in some cases. For fire-rated panels, silicone sealants are usually required. The important caveat for all of these sealants is that they are most successfully installed when they’ve been stored within acceptable temperature ranges. In cold weather, they may need to be kept in a warming bin; in warm weather they must be kept out of direct sunlight.
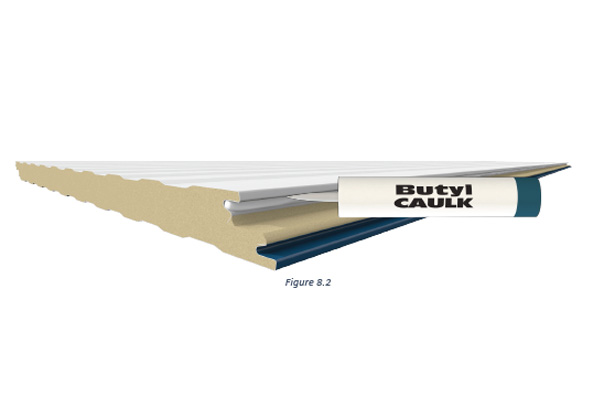

Tools to Use
Applying any of the needed sealants will require using the proper tools. Manual caulking guns don’t provide the consistent quality of application needed, so electric or pneumatically operated applicators are required.
Sealant Location
For typical building applications (non-freezer/coolers), the vapor sealant is placed in the interior panel joints when IMPs are installed vertically. For refrigerated spaces, the sealant is commonly placed on the exterior. If the IMPs are installed horizontally, then it usually is sealed on both the interior and the exterior panel joints to help with weather sealing as well. Note that the final placement of the sealant, as well as type and location, is actually the responsibility of the mechanical contractor/architect and not the panel supplier as it is to be based also on the mechanical design of the building envelope. In addition, the entire perimeter of the panels where they meet the building structure needs to be sealed. This includes the base flashing, interior corner trim, and eave struts. Further, marriage beads of butyl sealant must be placed at all panel terminations.
Sealant Continuity
In order to be effective, all sealant and caulking must be fully continuous. That means that the thickness of the sealant bead must be consistent and thick enough to fully close all gaps between or around IMPs. It should not be overdone, however, since too much sealant will ooze out between panels that are pressed together, causing a bit of a mess on one side of the other. Sealant continuity also means that it can not be interrupted due to poor adhesion. Therefore, before any sealant is installed, the application surfaces must be cleaned and dry to be sure that full adhesion is achieved. Always check with the panel suppliers details for minimum bead size and critical locations.
Factory-Installed Option for IMP
Some IMP manufacturers offer the option of having sealant pre-installed along the edges of the IMPs. Since the panels are wrapped and sealed for shipping, the sealant is protected and should be ready for use onsite. However, in this case, it is incumbent on the installers to handle the panels quite carefully, since the inadvertent placement of a hand over the sealant can damage it or deform it enough to render it ineffective. This factory-installed option offers a labor saving in the field but must be checked during installation and can be impacted by time climate depending on the time of year. Field application, while requiring more labor, does provide greater onsite flexibility for installers. Nonetheless, in all instances, the installer must ensure the sealants are properly located.
By paying attention to the details of sealing and caulking, a metal building constructed with IMPs will be a quality installation that will hold up quite well over time. To find out more about IMP metal products and systems that can help your next building be more vapor- and weathertight, contact your local MBCI representative.

