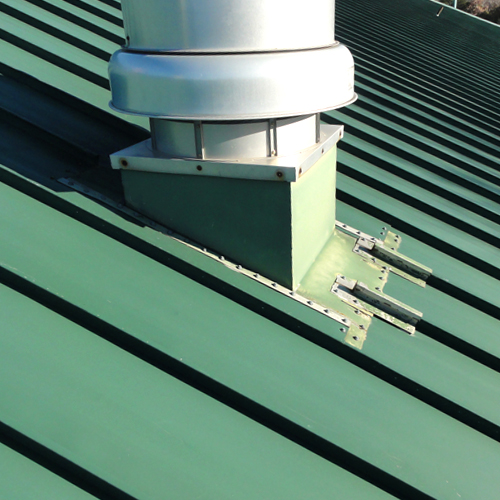
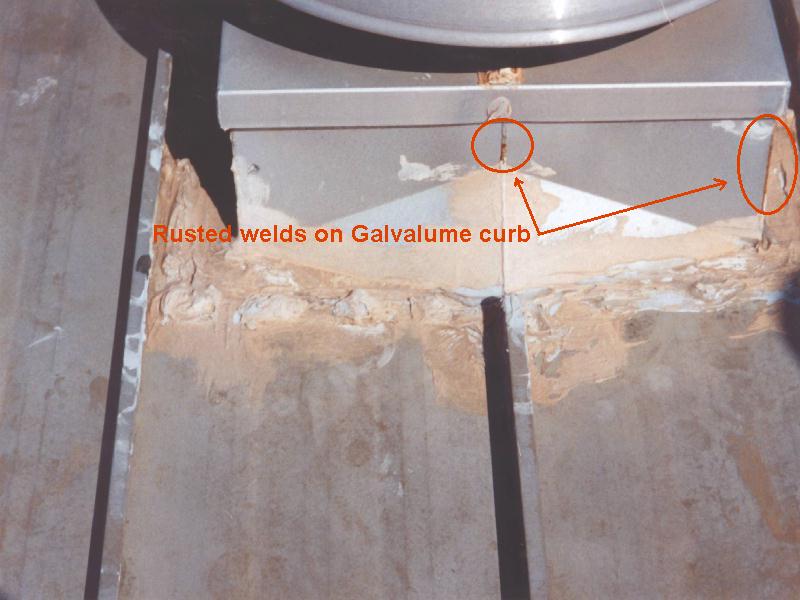
Are you involved with a building project along the Gulf Coast of Texas in which metal roofing or siding is involved? If so, obtaining a building permit may be subject to compliance with the Texas Department of Insurance (TDI) Windstorm Inspection Program. Here is some information that can help.
What is the TDI Windstorm Inspection Program?
In 1987, the Texas Legislature enacted HB 2012 with a requirement to mitigate losses to structures due to hurricanes along the Texas Gulf Coast. On January 1, 1988, the Texas Department of Insurance (TDI) began administrating the Windstorm Inspection Program in support of this legislation. The program is centered in Austin, with four other field offices also located along the Gulf Coast.
Where does the TDI Windstorm Inspection Program apply?
The Windstorm Inspection Program applies to all commercial and residential structures located primarily along the Gulf Coast of Texas. TDI has designated specific areas as catastrophe areas, also known as Texas’ First Tier Countries. The affected countries include Aransas, Brazoria, Calhoun, Cameron, Chambers, Galveston, Jefferson, Kenedy, Kleberg, Matagorda, Nueces, Refugio, San Patricio, Willacy and certain cities east of State Highway 146 in Harris County (La Porte, Morgan’s Point, Pasadena, Seabrook, Shoreacres).
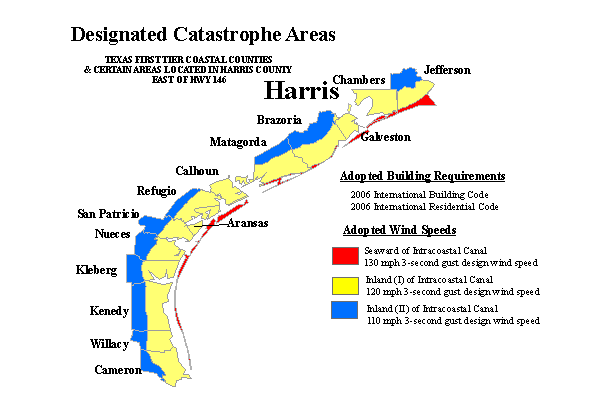
What is the Texas Windstorm Insurance Association?
The designated catastrophe areas often use Texas Windstorm Insurance Association (TWIA) as the insurer of last resort for the wind and hail portion of their building insurance. To qualify for wind and hail insurance through TWIA, all new structures plus any alterations, additions, or repairs to existing structures (including re-roofs or roof repairs) located in the designated catastrophe areas must be constructed and inspected according to the building specifications adopted by TDI.
How are Building Permits Affected?
All building work needs to meet the requirements of the adopted building codes in Texas (currently the 2006 version of the International Building Code and the International Residential Code). However, in addition to the codes, the TDI requirements must also be complied with in the designated countries. This is similar to other parts of the country that experience severe weather events (e.g., Dade County, Florida) where additional requirements above the code have been instituted for safety reasons. At the time of building permit application, evidence will need to be shown of TDI compliance in design documents; therefore, many times the local TDI office is contracted first and an application is submitted (Form WPI-1). Then, during construction, a TDI certified inspector (usually an engineer) will inspect the work, as will the regular building inspectors. Compliance will need to be shown with the TDI requirements (Form WPI-8) in order to obtain final sign off and a Certificate of Occupancy.
What Building Products are Approved for Use?
In order to be compliant with TDI standards, building products must be independently tested and shown to be able to withstand different levels of severe weather. For products like metal roofing and siding, the testing needs to include the method of attachment and the substrate type (metal, wood, etc.). Product evaluations are available by product type (such as “Exterior Coverings” for metal siding or “Roof Coverings” for metal roofing) and then by manufacturer all by either contacting a local TDI field office or on TDI’s website: www.texas.gov/wind/prod/index
For more information on this program visit http://www.tdi.texas.gov/wind/index.html or email Windstrom@tdi.texas.gov. To find out more about metal roofing and siding products that meet the severe weather requirements, contact your local MBCI representative.

