The installation of a new metal roof or wall panel on a residential home, business or commercial building takes care, precision and—of course—the right tools. Regardless of the structure, you’ll likely find that choosing the correct mechanical fastener plays a key role in the long-term performance, durability and efficacy of the project.
Many metal roof and wall panels, in fact, rely upon the use of quality mechanical fasteners to secure components to a structure. In order to guarantee a resilient and weather-tight attachment, it behooves the user to select an appropriately compatible fastener type for the specific metal construction, thereby ensuring expected benefits, such as energy efficiency, extended life cycle, and even lowering insurance bills for the owner. In other words, once the decision has been made to use metal building materials for your roof or wall project, the next step is figuring out how to hold it all together.
Know Your Fastener Options
Before selecting fasteners for the project, it is important for the designer or installer to understand the various materials and options available. Typically, this involves the following considerations:
- What type of material and coating is appropriate?
- What type of head do I need? Does it need to be painted?
- Do I need a washer? If so, what material should I use?
- Should I use self-tapping or self-drilling screws?
- What thread count should I specify?
- How long does the fastener need to be?
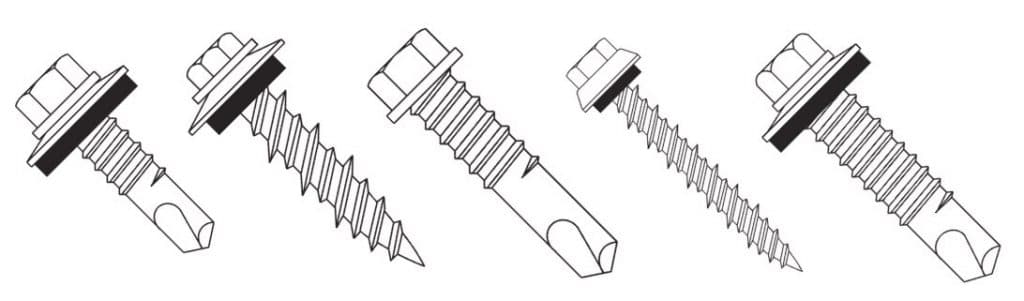
Select a Fastener on the Basis of Material
Most fasteners are made from coated metal but both the type of metal and coating must be chosen on the basis of the materials the fastener is bringing together. Galvanic action between dissimilar metals can cause premature fastener failure and lead to leakage. Even stainless steel screws will corrode severely under the right (or actually wrong) conditions. In extreme exposure, sometimes the best option is to use galvanized screws and plan on replacing them at a later date with a larger screw once the zinc has been depleted.
Considerations for Self-Drilling Screws
Self-drilling screws have a drill bit built in and don’t require a pre-drilled hole. Although self-drillers save the installer the step of drilling a hole, they are not always a good idea. The available space between the back of the hole and the next physical restriction must be at least as big as the bit itself or the threads will not engage. Also, drilling a hole allows a quick inspection to ensure the hole is in the correct location and plies are aligned and parallel. Generally, self-drillers are used when going through thin gauge steel into thicker gauge steel and self-tappers are used when fastening two thin gauge plies.
Washers
Fasteners may be used with or without washers. While plastic washers help prevent leaks, they are not required on purely structural connections. When using washers, it is important to visually inspect the screw after installation to be sure they are properly compressed and not kinked. Exposed plastics generally degrade when exposed to ultraviolet light. Furthermore, use of neoprene washers may be prevented by restricted material lists, or “red lists.” Fastener heads themselves may be made of different materials than the rest of the screw, long-life ZAC heads being the most common example.
Fastener Profiles
Fasteners have different profiles. Flat or “pancake” screws are used when low profile installation is necessary and may have Philips, hex, or Torx sockets. Which socket to use is usually an installer’s preference based on accessibility restrictions. Another common feature is an over-sized dome beneath the head to encompass a larger washer. Also called shoulder screws, these screws are useful when thermal movement might distort the holes.

Thread Count per Inch
Thread count per inch, or TPI, must also be considered. Most commonly, fasteners are installed through the thinner ply first and grip in the thicker ply, pulling the plies together. Therefore, TPI selection is usually driven by the thickness of the thicker ply. Generally, the TPI is close to the gauge of the metal for gauge steel and higher for plate and sheet.
Length
The fastener must also be long enough to fully engage all plies of material, plus the length of the drill bit in the case of self-drillers. Generally, this is rounded up to the next half or quarter inch. However, the longer the screw, the more torsional strain is produced during driving and in the case of very long fasteners, this can break the fastener or introduce wobble, leading to poor installation. Therefore, stainless steel with over-sized washers is often used for long screws for added strength and protection.
For More Information on Fastener Compatibility
To learn more about fasteners and their compatibility with different types of metal roof or wall panels, check out Metal Construction Association’s recently published technical bulletin, Fastener Compatibility with Profiled Metal Roof and Wall Panels.
