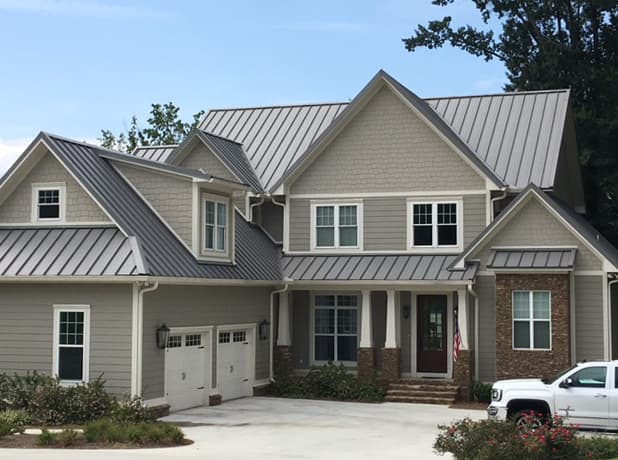
The primary purpose of a building’s envelope (roof and walls) is to protect the building’s interior spaces from the exterior environment and provide the desired exterior aesthetics. Whether choosing insulated metal panels (IMPs) for their superior performance or, instead, looking to the wide range of aesthetic choices available with single-skin panels—or some combination of the two—the common goal must always be to protect the building from the potential ravages of water, air, vapor, and thermal/heat. By ensuring proper installation of metal panels and, thereby, properly sealing the building envelope, problems can be mitigated, efficiencies maximized, and the integrity of the building protected.
Here, we’ll briefly consider the benefits of each panel, and some key considerations relative to their sealant needs and capabilities.
Insulated Metal Panels (IMPs)
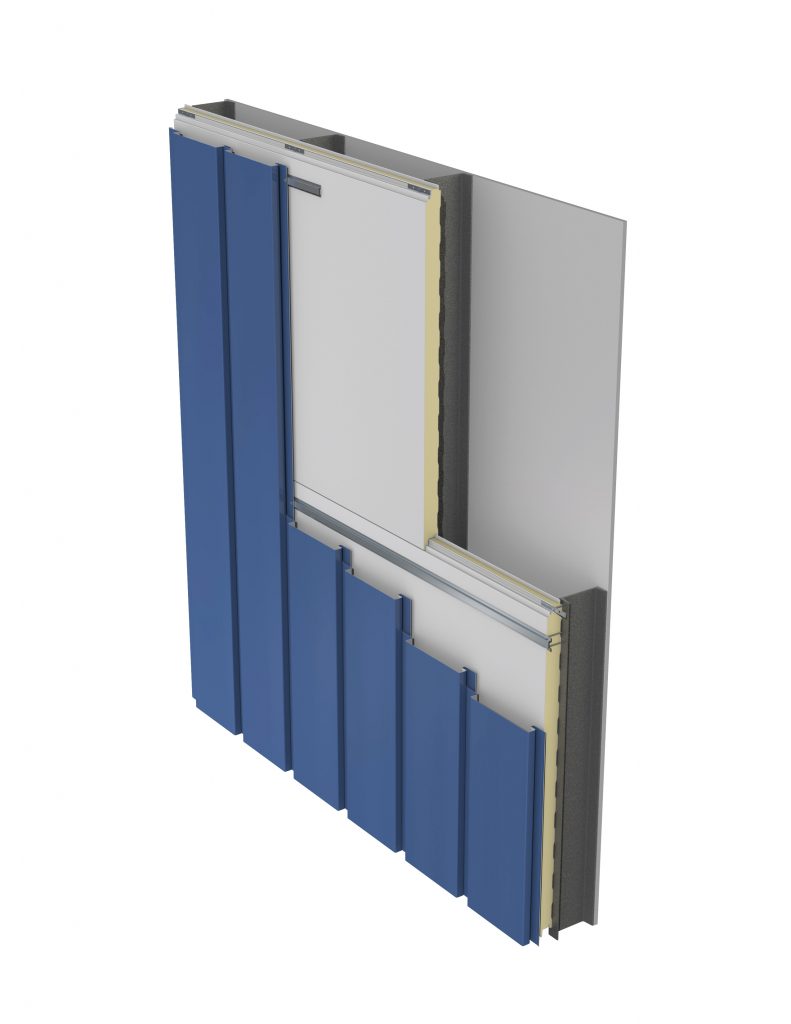
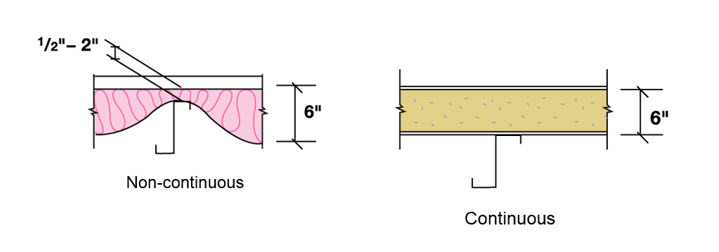
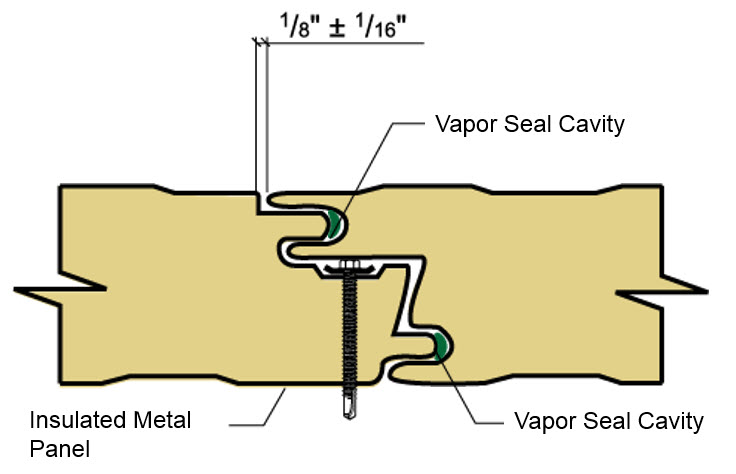
IMPs are lightweight, composite exterior wall and roof panels that have metal skins and an insulating foam core. They have superior insulating properties, excellent spanning capabilities, and shorter installation time and cost savings due to the all-in-one insulation and cladding. In effect, IMPs serve as an all-in-one air and water barrier, and are an excellent option for retrofits and new construction. With their continuous insulation, roof and wall IMPs provide performance and durability, as well as many aesthetic benefits.

Generally speaking, because of the nature of the joinery, it is easier to get a good seal in place with IMPs given their relative simplicity (i.e., putting the two pieces together with the sealant). They require great attention, though, in terms of air and vapor sealing—aspects largely controlled by the installers on a given project. As an example, vapor sealing in cold climates or applications is critical to the overall soundness of a building. Consider the damage a building could incur if moisture seeps into a panel and becomes trapped; it if freezes, it could push panels out of alignment. This would result in not just an unattractive aesthetic, but a performance failure as well. In order to be effective, all sealant and caulking must be fully continuous.
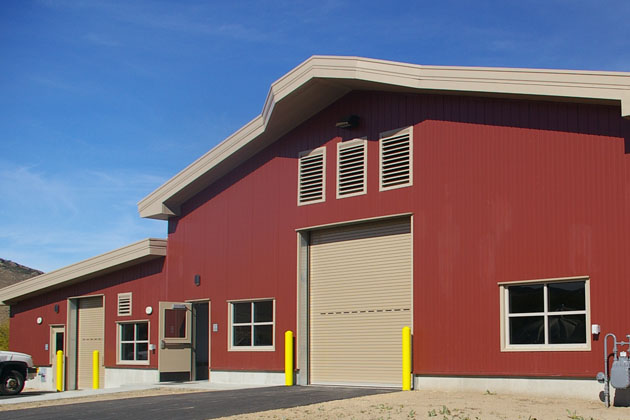
Single-Skin Panels
Single-skin panels, alternatively, offer the advantage of an expansive array of colors, textures and profiles. They are also thought to have more “sophisticated” aesthetics than IMPs. Single-skin panels are available in both concealed fastener and exposed fastener varieties, and are part of an assembly. They can be used alone or in combination with IMPs, and as long as the needed insulation is incorporated, single-skin panels can meet technical and code requirements, depending on the application. Single-skin products offer a wide range of metal roof systems and wall systems as well.
Getting the proper seal on single-skin panels may require extra sealants or closures, and have more parts and pieces that have to come together to create the seal. However, when properly installed and sealed, they can provide excellent performance in their own right. Some key caveats include ensuring panel laps are properly sealed with either tape or gun butyl sealants, and carefully inspecting air and water barriers for proper installation as well as penetrations through the wall for sealing/fire caulking prior to panel.
In most cases, following the details for the most common conditions will give you a successful and high-performing outcome.
Regardless of the type of metal panel used, taking the time and effort to ensure the sealing and caulking details are properly handled, metal buildings can protect the built environment and provide long-lasting quality and performance.